According to the Exploding Topics web resource, about 1 mln users resorted to ChatGPT’s help for the last five days. Indeed, thanks to the hype that this tool regularly creates in the Internet community, interest in artificial intelligence technologies has increased significantly, both in everyday use and in the context of implementation in regular business processes. In particular, today, many companies, pioneering the supply of proprietary AI-powered tools, such as Nvidia, are actively developing solutions for scaling the computing power that AI consumes. This raises a completely logical question – perhaps, now, it makes sense for miners to diversify their income sources with high-performance AI computing?
Generally speaking, given the growth of shares of companies such as OpenAI, Nvidia, Meta, Arista Networks, etc., i.e., those who allocate more and more of their resources to innovative developments in the field of artificial intelligence, it becomes clear that, being supported by the public around the world, this trend will only intensify in the coming years. Moreover, if we take into account the fact that many businesses, regardless of their size, use AI for automation to reduce operating costs, the infrastructure that supports these solutions will also inevitably scale over time.
As for miners, just in the last month, they shared a lot of posts in the media, where it is stated that they are going to use generative AI in their regular business tasks. That is why no one can say that AI is just hype anymore because all that remains for them is to simply remain indifferent to this technology. But is it worth it?
So, to find it out, let’s get inspired by the insights of Sergey Gerasimovich, CEO of EZ Blockchain, who attended the Nvidia GTC 2024 conference and is ready to share his newly acquired knowledge on the high-performance AI computing vs Bitcoin mining comparison.
AI Hardware and Architecture
AI, as we all know, is about developing systems that can replicate human intelligence. Specifically, it relies on technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing, which use data centers with powerful computing clusters that connect multiple servers via high-speed networks to enable efficient parallel processing. Such systems often use specialized chips, including graphics processing units (GPUs) and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). In addition, specialized AI hardware such as tensor processing units (TPUs) and other specialized chips, is growing in popularity as well.
Key Similarities and Differences Between Bitcoin Mining and AI HPC
On the one hand, based on the above, mining is in many ways similar to how computing power works that supports AI solutions. However, given the difference in their tasks and the technologies used, they still cannot be called identical. So, let’s find out how exactly they are the same and how they differ.
5 key Similarities:
- Significant power consumption. Both Bitcoin mining and AI HPC data centers consume enormous amounts of power when fully operational, which is required by ASIC miners and GPUs to operate.
- Need for cooling. Both of these processes generate large amounts of waste heat caused by hardware that performs intensive computing operations. Thus, to maintain the health of this hardware and, in general, the optimal temperature conditions inside the premises where it is located, their owners have to install specialized cooling systems.
- Hardware performance optimization. Each of these processes can maximize their efficiency and computing speed by optimizing the hardware.
- Introducing innovative technologies. Bitcoin mining and AI HPC centers that are looking to continually increase their computing powers can benefit from introducing innovative technologies aimed at achieving a better balance between performance and cost efficiency. For example, we can include in this category the latest developments in the areas of optimization algorithms, hardware design, cooling systems, and resource efficiency.
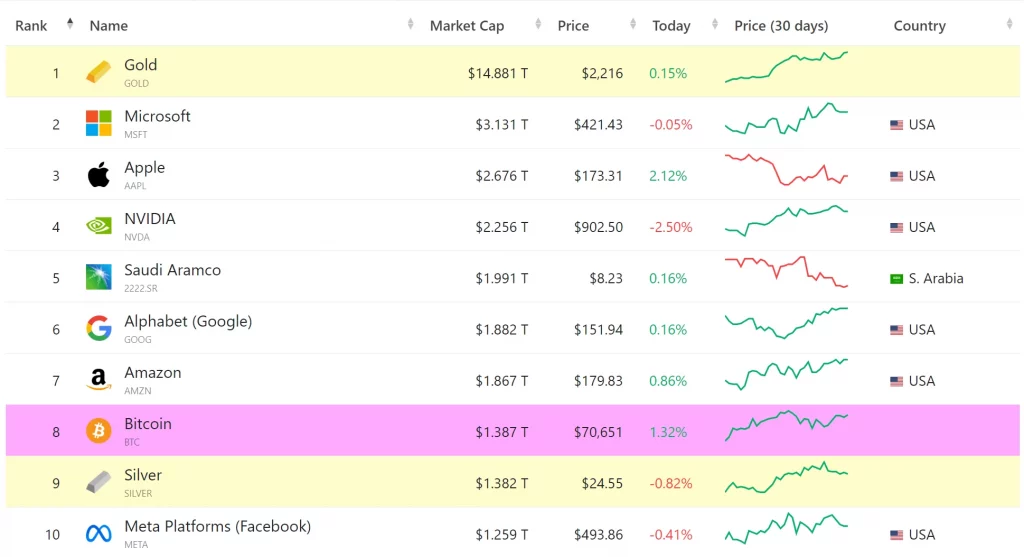
Dominance in the international hardware market. As you may know, among miners, Bitmain is considered the most famous manufacturer as this company supplies high-performance ASIC miners all over the world. Thanks to this, today, its market share is estimated at more than 76%. In turn, Nvidia can boast a market share of 82% among manufacturers of discrete video cards with a capitalization of 2.2 trillion dollars (by the way, these figures brought Nvidia an honorable third place in its size after such whales as Microsoft and Apple). Of course, competitors are not asleep, and in the coming years, we can expect new startups in these industries, but whether they will be able to displace Bitmain and Nvidia from their pedestals remains doubtful.
5 Key Differences:
- Primary goal. Bitcoin miners verify transactions on the network and are rewarded with new coins and fees. As for AI HPC centers, they provide computing power for tasks such as training neural networks, processing large amounts of data, and running complex AI algorithms.
- Financial model. Bitcoin miners earn money by mining and providing hosting services. In turn, AI HPC centers earn income by renting out computing power, where their clients pay for resources as they use them or rent hardware and software for a fixed period of time.
- Infrastructure requirements. Mining facilities operate with intermittent loads, and the average uptime rate in the industry is 95%. It is also worth noting that some operators deliberately allow more than 5% downtime to participate in energy management programs and more profitable tariffs. When it comes to AI HPC systems, they require significantly higher availability – typically 99% or higher, which is understandable given their role in supporting IT infrastructures for mission-critical areas such as finance, medicine, or defense technologies (in which case, according to some laws, it can exceed 99.9%). In this regard, to avoid downtime, HPC operators have to additionally use backup power systems and look for more efficient cooling approaches – for example, those implemented in liquid cooling systems (as opposed to air cooling systems, which are often used by Bitcoin miners).
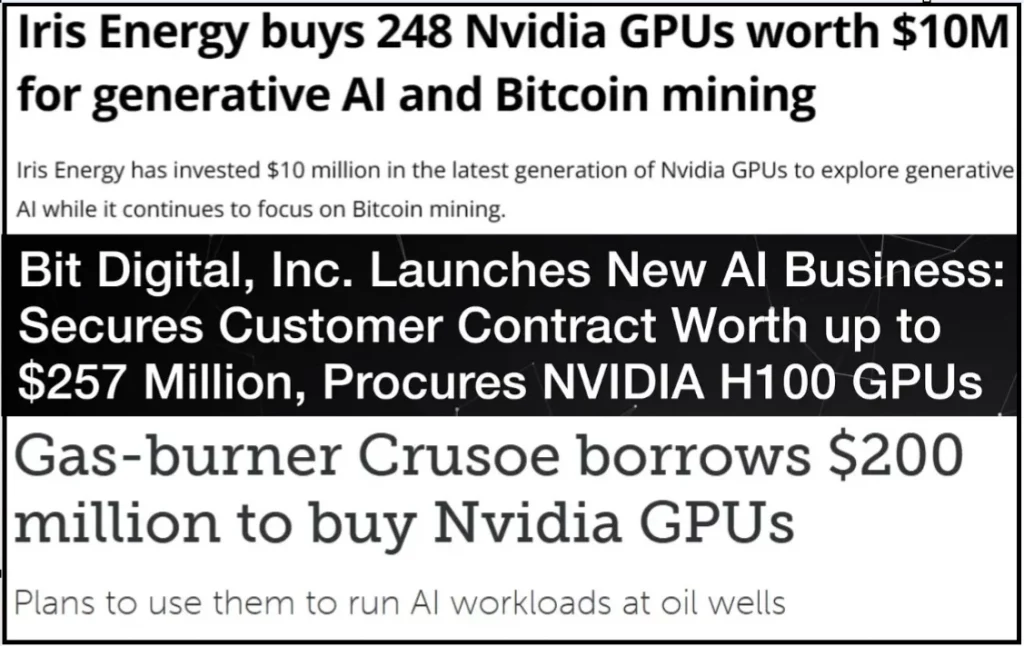
- Initial investment. Deploying high-performance data centers requires significant investment, but 2024 will be remembered for the fact that the cost of ASIC miners has become very low due to market overcrowding. At the same time, the demand for GPUs for AI HPC has grown rapidly over the past year, as leading tech corporations began to purchase video cards en masse to provide capacity for their AI services. Thus, such increased demand has irreversibly led to a shortage of equipment and a rapid increase in prices.
- Market trends. How much mining can bring in terms of profit is influenced by many factors – from the BTC rate and network complexity to the cost of electricity and equipment efficiency. At the same time, the demand for AI HPC services is determined by slightly different aspects, such as the intensity of AI development in certain sectors, investment in AI research, and competition among cloud computing providers.
Based on the above, we can conclude that despite similar requirements for power supply, cooling, and hardware, mining farms, and AI HPC centers differ radically in their goals, business models, equipment costs, and dependence on market trends.
Why Bitcoin Miners are Integrating AI HPC Services into Their Business
In recent months, several major mining companies have made the decision to publicly announce their plans to integrate AI and high-performance computing solutions into their regular business processes to diversify their revenue sources, reduce dependence on one direction, and strengthen their competitive position in such a dynamic industry.
Honestly, this is not surprising, as to achieve the above goals, they must have profitable business models in reserve beyond hosting services for Bitcoin mining, namely, providing computing power for AI. If we add to this that this source of income is completely unaffected by fluctuations in the price of Bitcoin or changes in network difficulty, it becomes clear that a business that has expanded its activities to this model becomes much more sustainable. Finally, receiving income in a centralized currency (for example, in dollars) provides increased flexibility in the strategy of holding BTC since now, miners will be able to sell it at the most profitable moments.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that when cryptocurrency mining becomes economically unviable due to changes in legislation, decreased demand, or under the influence of any other external factors, the development of HPC-based AI services can ensure the company’s viability, reducing the risks of closing its data centers or their forced relocation to regions with greater mining potential.
Investing in AI HPC vs Bitcoin Mining
If you are a retail investor interested in AI HPC, there are a few options you should consider:
- Investing in technology companies. The first place to start your research is by assessing the investment potential of publicly traded companies that develop AI algorithms, provide HPC infrastructure, or create brand-new AI solutions for businesses. Some examples of such companies include the aforementioned Nvidia, as well as Intel, AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
- ETFs and mutual funds. If you are pursuing a strategy that involves maximum diversification of your portfolio, you may want to consider exchange-traded funds (ETFs) focused on AI and advanced technologies. Examples of such funds include the Global X Robotics & Artificial Intelligence ETF (BOTZ), ARK Innovation ETF (ARKK), and iShares PHLX Semiconductor ETF (SOXX).
You can also consider participating in venture funds, angel investment platforms, and crowdfunding – following this approach, you will have the opportunity to invest in promising AI and HPC startups at the early stages of their development. On the other hand, this approach is the riskiest of all described here, which can be explained by the startups’ instability. Finally, instead of deploying your own HPC infrastructure, you can consider participating in cryptocurrency mining. This is possible both through purchasing a share in a mining company and by financing mining in exchange for a share of the profits.
Generally speaking, small investors have a fairly low entry threshold for Bitcoin mining due to the ability to purchase a separate mining rig as part of hosting services or simply use cloud mining services (it is important to note that the second option, being cheaper, still reduces control over the mining process). That is why, before making any investment decision, you should thoroughly analyze the market, assess all possible risks, determine your financial goals, and, best of all, consult with a specialist in this field, especially if you are a beginner.